Broken SSL/TLS certificate chains from missing intermediates can cause trust errors. Learn how to diagnose and fix them by installing a complete chain.
Browser Trust Errors
If you have installed a new SSL/TLS certificate on your web server but visitors are experiencing browser trust errors such as Not Secure, or Your Connection Is Not Private, please make sure that a complete intermediate certificate chain has been installed. In Google Chrome, a common error message of this type is NET::ERR_CERT_AUTHORITY_INVALID.
All of the following browser errors resulted from installing a valid certificate, but with a broken chain caused by missing intermediates:

Not Secure trust warning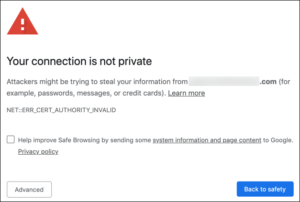
NET::ERR_CERT_AUTHORITY_INVALID trust warning in Chrome browser window.
This Connection Is Not Private.
For more examples of browser error messages* resulting from missing intermediate certificates, please refer to our guide on Troubleshooting SSL/TLS Browser Errors and Warnings.
Additionally, Firefox caches intermediate certificates in its own certificate store; if you previously visited a website that included any intermediates missing from your server, Firefox will use them to make a complete certificate chain when necessary. This enhanced behavior means Firefox users experience fewer certificate chain errors compared to other browsers.
*Error messages and browser interfaces shown may vary slightly across different browser versions and operating systems. The fundamental symptoms of missing intermediate certificates remain consistent across all platforms.
Diagnosing the Problem
Diagnostic Tools and Methods
You can check for missing intermediate certificates using several methods:
- Online SSL Checkers
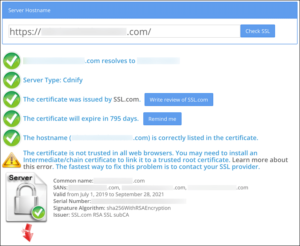
- SSL Shopper’s SSL Checker remains an excellent tool for identifying missing intermediates. The screenshot below reveals the situation that produced the errors shown above. Modern SSL checking tools provide comprehensive analysis, including chain completeness, expiration dates, Extended Key Usage validation, and compatibility with current browser requirements.
- Modern SSL testing tools also check for upcoming expiration dates and Extended Key Usage issues.
Browser Developer Tools
Most browsers now provide enhanced certificate inspection capabilities through their developer consoles. In Chrome, Firefox, and Safari, you can access detailed certificate chain information by:
- Clicking the lock icon in the address bar
- Selecting “Certificate” or “Connection is secure”
- Viewing the complete certificate chain and validity details
Command Line Tools
For server administrators, OpenSSL provides comprehensive certificate chain analysis:
openssl s_client -connect example.com:443 -showcerts
openssl s_client -connect example.com:443 -showcerts
Understanding Certificate Validity Changes
The SSL/TLS certificate landscape has evolved significantly in recent years, with important changes affecting certificate lifespans and usage:
Shortened Certificate Lifespans
Since September 2020, major browsers no longer trust SSL/TLS certificates with validity periods longer than 398 days (approximately one year). The CA/Browser Forum has adopted a phased schedule (Ballot SC-081v3) to reduce maximum TLS certificate lifetimes: 200 days for certificates issued on/after March 15, 2026, 100 days on/after March 15, 2027, and 47 days on/after March 15, 2029.
These changes necessitate the implementation of robust certificate management and automation systems.
Extended Key Usage Restrictions
Chrome Root Program policy requires that, beginning June 15, 2026, newly issued publicly trusted TLS server certificates include only the serverAuth EKU (no clientAuth).
Major CAs are aligning ahead of this date. If you require TLS client authentication, use separate client-auth certificates from a private or dedicated hierarchy. Organizations using certificates for both purposes will need separate certificates for each function.
Solving the Problem
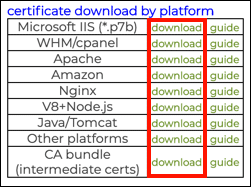
When you download your certificate from your SSL.com user account using the link for your server platform, you receive a zipped file that includes both the certificate and any necessary supporting files. If you only wish to download the intermediate certificates, you can also use the CA bundle download link.
Installation of intermediates varies by server platform. For specific instructions on how to install the required intermediate certificates on your server and create a complete chain, please refer to our certificate installation documentation.
Impact on Installation
When downloading certificates from your SSL.com account, ensure you’re using the most current intermediate certificates. The CA bundle download link in your account will always provide the correct, up-to-date intermediate certificates for your installation.
Modern Installation Best Practices
Automation is Essential: With decreasing certificate lifespans, manual certificate management becomes increasingly impractical. Consider implementing:
- Automated certificate renewal systems (ACME protocol clients)
- Certificate lifecycle management tools
- Monitoring systems that alert before certificate expiration
Platform Considerations:
- Many hosting providers and CDNs now automatically manage intermediate certificate installation
- Cloud platforms often provide integrated certificate management services
- For on-premises installations, ensure your renewal process includes intermediate certificate updates
Verification Steps – Always verify your complete certificate chain after installation:
- Test from multiple browsers and devices
- Use SSL checker tools to confirm chain completeness
- Verify certificate validity periods align with your renewal schedule
- Check that certificates contain only appropriate Extended Key Usage values
Confirm the Fix
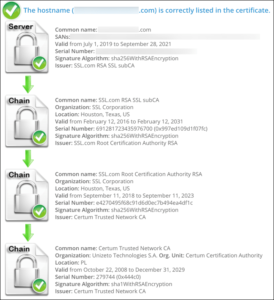
With all supporting certificates installed on the same server that produced the “not trusted” errors shown above, SSL Checker shows a complete chain, and the browser trust errors are gone:
Future-Proofing Your Certificate Management
Prepare for Shorter Lifecycles
- Implement automated certificate management systems before the 47-day validity period takes effect in 2029
- Establish monitoring and alerting for certificate expiration
- Consider using ACME-compatible certificate authorities for seamless automation
Separate Authentication Types
- Plan to separate server authentication and client authentication certificates
- Review current certificate usage to identify mixed-use certificates
- Implement dedicated PKI hierarchies for different certificate purposes
Monitoring and Maintenance
- Regular audits of certificate inventories across your infrastructure
- Automated testing of certificate chain completeness
- Documentation of certificate dependencies and renewal procedures
The trend toward shorter certificate lifespans and stricter usage requirements emphasizes the critical importance of proper intermediate certificate installation and comprehensive certificate lifecycle management.
Proper intermediate certificate installation remains fundamental to SSL/TLS security; however, the landscape continues to evolve with shorter certificate lifespans and stricter browser requirements.
By following current best practices, implementing appropriate automation, and staying informed about industry changes, you can ensure your certificates provide reliable security for your users.
For the most current certificate installation instructions and intermediate certificate bundles, always refer to the documentation and download links in your SSL.com account, as these are regularly updated to reflect the latest requirements and CA changes.
Need Help? SSL.com’s support team stays current with all industry changes and can assist with certificate installation, chain configuration, and preparation for upcoming requirements. Contact us at Support@SSL.com or use the chat feature at the bottom right of this page.